Customizing Compile-time Diagnostics
前不久,Eric Niebler 提升了 stdexec 的编译期诊断信息。他利用了 concept 在评估失败时编译器会打印出模板参数类型的特征,让那些查询类型属性的 trait 返回一个他定制的模板类,然后诊断消息命名成类名作为模板参数打印出来,而不是仅仅返回一个布尔值。
// #include <concepts>
#include <type_traits>
// struct compile_error<What, With...>
//=====================================
struct none;
template <class What, class... With>
struct compile_error : std::false_type
{
using type = compile_error;
};
template <>
struct compile_error<none> : std::true_type
{
using type = compile_error;
};
// concept error<T>
// concept no_error<T>
//=====================================
namespace detail {
consteval compile_error<none> get_error(...);
template <class What, class... With>
consteval compile_error<What, With...> get_error(const compile_error<What, With...>*);
template <class T>
extern decltype(get_error((T*)nullptr)) error_v;
template <class T>
using error_t = decltype(error_v<T>);
template <class T>
concept error_impl = (not T{});
template <class T>
concept error = error_impl<error_t<T>>;
template <class T>
concept no_error_impl = T{};
template <class T>
concept no_error = no_error_impl<error_t<T>>;
} // namespace detail
using detail::error;
using detail::no_error;
// Usage
//=======
struct NOT_CALLABLE;
template <class T>
struct WITH_SIGNATURE;
template <class T>
struct is_function : std::conditional_t<std::is_function_v<T>,
std::true_type,
compile_error<NOT_CALLABLE, WITH_SIGNATURE<T>>>
{
};
template <class T>
inline constexpr bool is_function_v = is_function<T>::value;
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
template <class T>
#if defined(USE_COMPILE_ERROR)
requires no_error<is_function<T>>
#else
requires is_function_v<T>
#endif
void foo(T f)
{
}
int main() {
foo<int(int, int)>(add);
foo(add);
}
- 改进前:仅仅告知在哪个地方诊断失败。
- 改进后:不仅告知在哪个地方诊断失败,也说明原因。
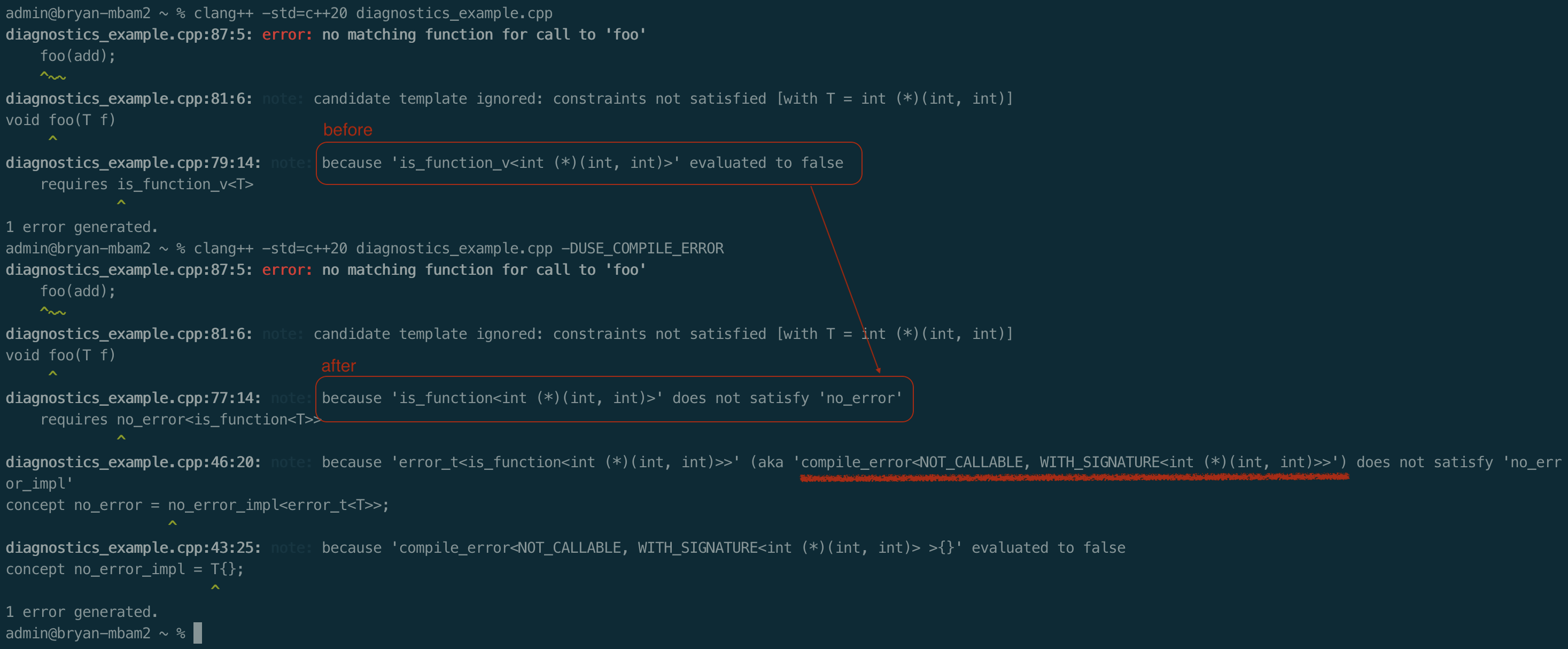
这看起来很好,但是使用时有点受限,比如查询类型属性的模板参数不能用表达式(如:decltype)来推断模板参数类型,而且必须使用 concept 来触发条件评估。如下示例就无法达到目的:
template <class T>
requires std::is_same_v<decltype(detail::error_v<is_function<T>>), compile_error<none>>
void foo(T f)
{
}
% clang++ -std=c++20 diagnostics_example.cpp
diagnostics_example.cpp:83:5: error: no matching function for call to 'foo'
foo(add);
^~~
diagnostics_example.cpp:77:6: note: candidate template ignored: constraints not satisfied [with T = int (*)(int, int)]
void foo(T f)
^
diagnostics_example.cpp:76:10: note: because 'std::is_same_v<decltype(detail::error_v<is_function<int (*)(int, int)> >), compile_error<none> >' evaluated to false
requires std::is_same_v<decltype(detail::error_v<is_function<T>>), compile_error<none>>
^
1 error generated.
